In industrial systems, pump type selection directly affects system stability, maintenance complexity, and long-term operating cost. Different pump types vary fundamentally in working principles, structural design, and applicable conditions. Understanding these differences is the foundation of proper selection.
From an engineering perspective, industrial pumps can be grouped into several representative structural and functional categories.
Centrifugal Industrial Pumps
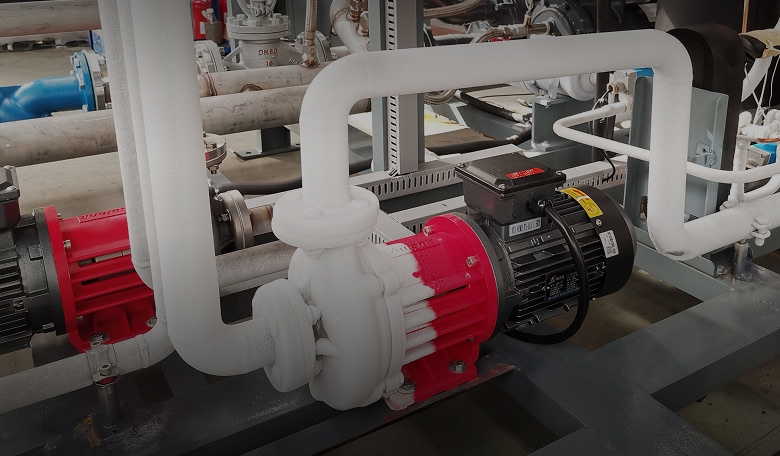
Centrifugal pumps use rotating impellers to accelerate fluid outward from the center, increasing pressure and flow. They are among the most widely used industrial pump types.
Common designs include end-suction pumps, self-priming pumps, multistage centrifugal pumps, and ANSI-standard process pumps. These pumps are well suited for low- to medium-viscosity media and are widely used in chemical solvents processing, thermal systems, and general industrial transfer.
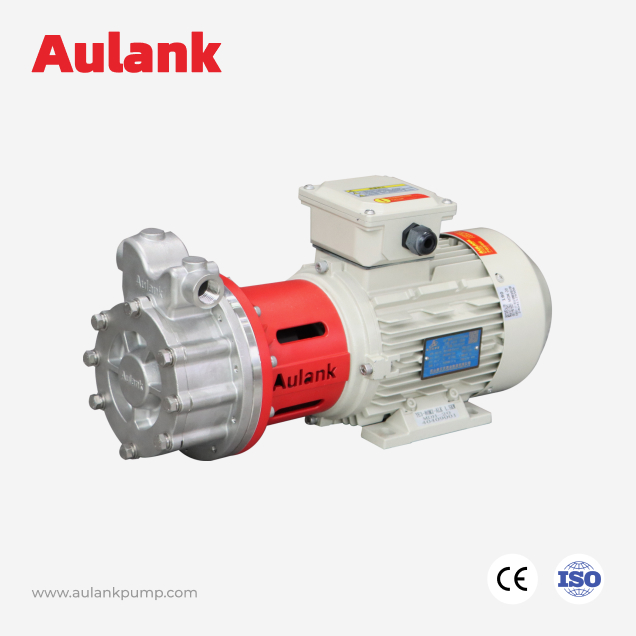
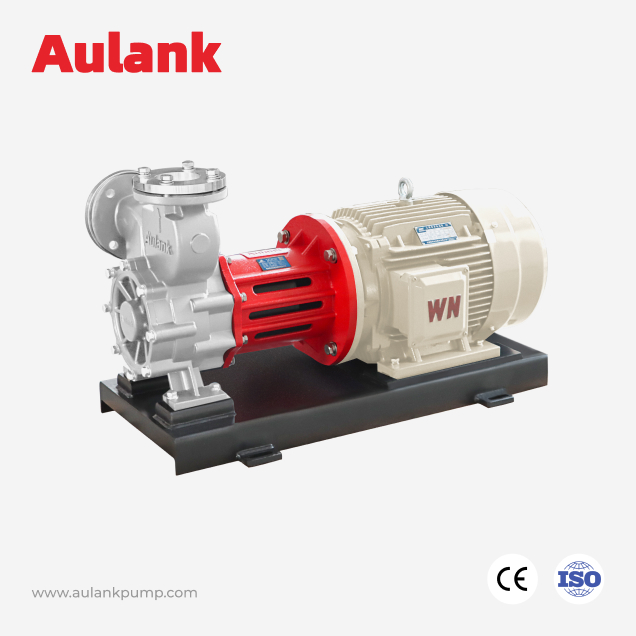
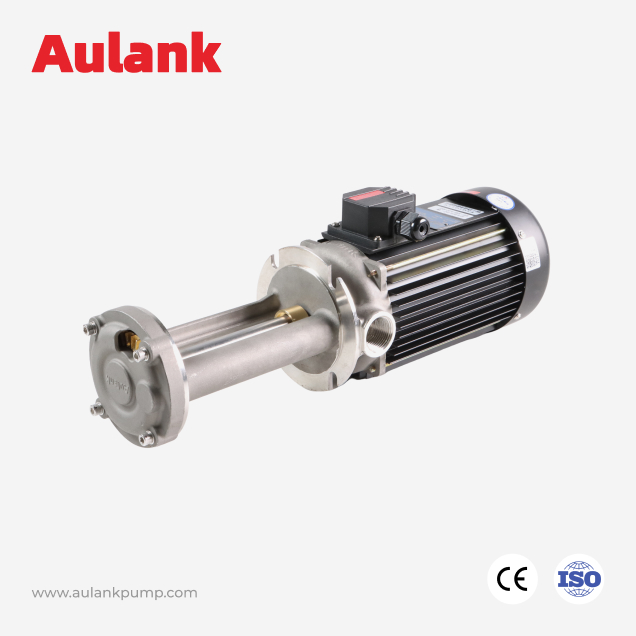
Aulank's mechanical seal and magnetic drive centrifugal pumps prioritize structural stability and material adaptability to support continuous operation and a wide temperature range.
Vortex and Micro-Flow Pumps
Vortex pumps are suitable for micro-flow, high-head, or space-constrained systems. They provide relatively stable pressure output at low flow rates and are commonly used in fine chemical processes, Semiconductor temperature control chiller, integrated temperature control for die-casting molds, microchannel reaction temperature control, and thermal control loops.
Featuring high-head and low-to-medium flow characteristics, our vortex pumps complement the performance range of traditional centrifugal pumps, filling the gap for high-pressure precision applications.
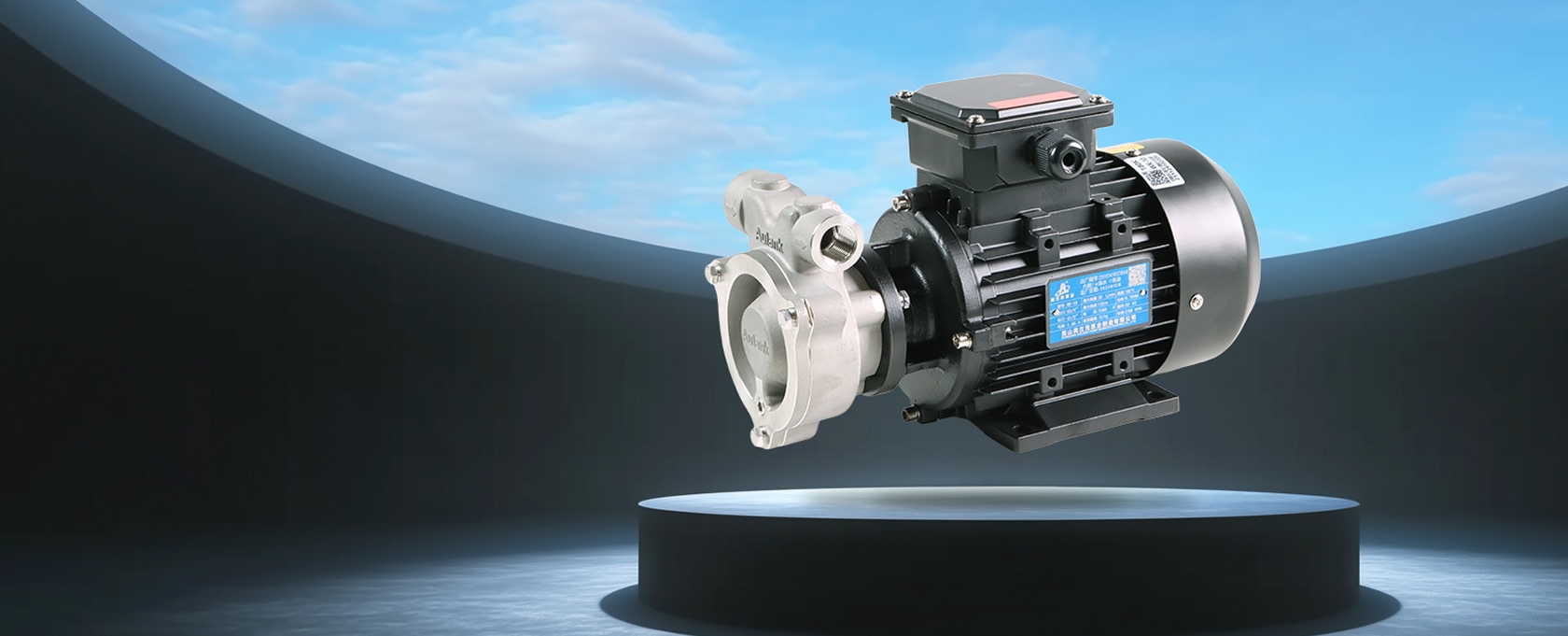
Positive Displacement Industrial Pumps
Positive displacement pumps deliver fluid through cyclic volume changes and include gear pumps, vane pumps, and screw pumps. Their primary advantages are stable metering conveying and strong pressure control.
They are especially suitable for high differential pressure, higher-viscosity media, or applications requiring accurate flow control.
Aulank focuses on magnetic-drive gear pump structures within this category for chemical solvents transfer and leakage-sensitive systems.
Specialized and System-Oriented Pumps
Certain industries require pumps designed for specific system conditions, such as abrasion-resistant pumps, hygienic process pumps, or vertically integrated system pumps.
These pumps are typically selected based on industry standards and system architecture rather than standard catalog comparison.
There is no universally superior pump type. The correct choice depends on alignment with actual operating conditions, media properties, and system objectives.
Learn more about Industrial Pump Types
Key Engineering Considerations in Industrial Pump Selection
Industrial pump selection is an engineering decision centered on system operating conditions rather than a simple product comparison. Proper selection requires balancing multiple constraints instead of focusing on a single performance metric.
Media Characteristics and Compatibility
Media physical and chemical properties form the basis of selection. Gas content, solids, volatility, and crystallization tendencies directly affect pump type and material configuration.
The same media may exhibit very different corrosion or lubrication behavior at different temperatures, making material selection dependent on actual operating conditions rather than media name alone.
Flow Rate and System Pressure
Flow and pressure should be evaluated within the context of the entire system. Valve operation, piping resistance changes, and process fluctuations all affect the actual operating point.
Engineering selection prioritizes stable long-term operation near the target duty point rather than short-term peak capability.
Environmental and Operating Conditions
Operating temperature, pressure boundaries, and thermal cycling influence structural design, sealing systems, and material lifespan.
High- and low-temperature applications require careful assessment of thermal expansion, seal stability, and startup conditions.
System Integration and Compatibility
Industrial pumps do not operate independently. Interface standards, installation orientation, space constraints, piping support, and control logic all affect performance.
Poor system integration often leads to vibration, noise, or abnormal wear even when pump parameters appear suitable.
Manufacturing and Technical Reliability
Selecting a manufacturer with proven R&D and manufacturing capability reduces long-term operational risk.
Aulank continuously invests in structural optimization, material matching, and application-driven engineering to support real industrial systems.
Energy Efficiency and Lifecycle Cost
Beyond meeting operating requirements, energy efficiency and maintenance cost are critical factors.
Proper selection can reduce energy consumption, maintenance frequency, and downtime, optimizing total lifecycle cost.
The objective of industrial pump selection is to achieve stable, predictable long-term operation within defined boundaries by integrating product parameters, system conditions, and application experience.
Learn more about aulank industrial pump solutions