Corrosion Resistant Pump Solutions for Aggressive Chemicals
Aulank provides specialized pumping solutions designed to withstand the attack of strong acids, alkalis, and aggressive chemical solvents. Targeting fluids such as Sulfuric Acid, Hydrochloric Acid, Nitric Acid, Hydrofluoric Acid, and various organic solvents, our pumps are engineered to prevent material degradation. By utilizing advanced inert materials and specialized structures, we ensure process continuity where standard metal pumps would fail rapidly.
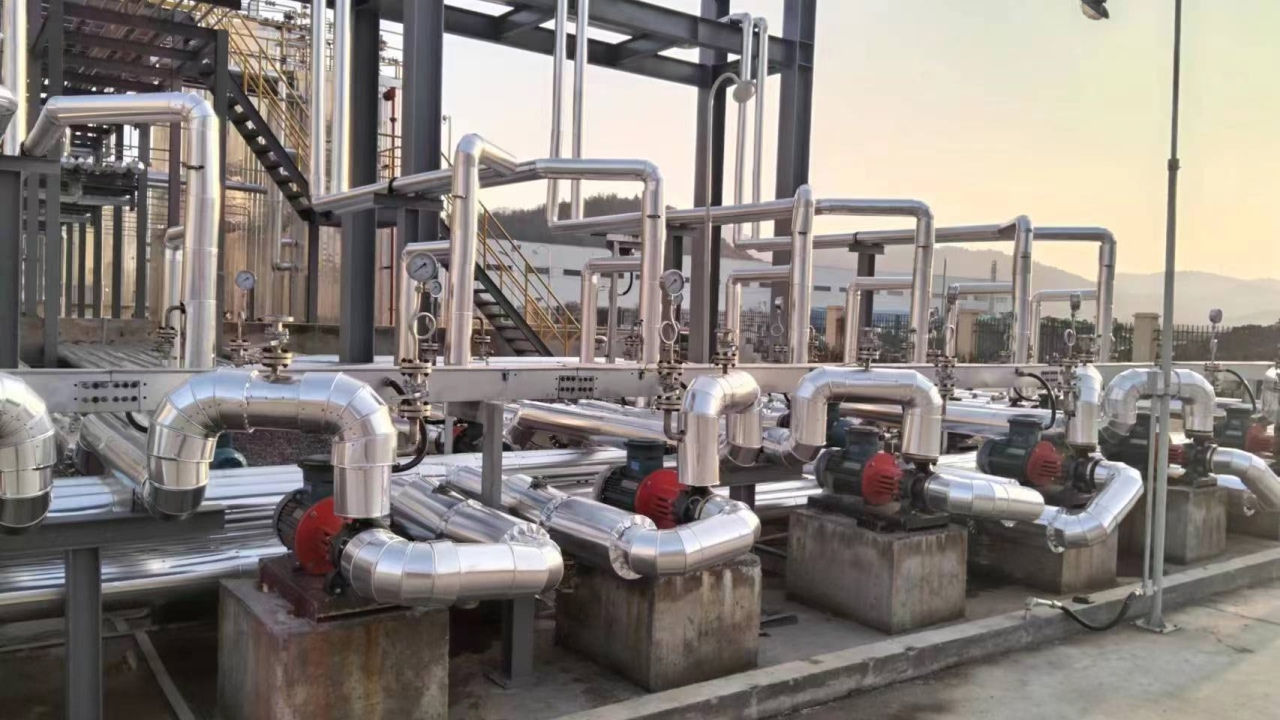

Pump Types & Working Principles
Magnetic Drive Pump (Sealless Design)
- Working Principle: This pump operates on the principle of magnetic coupling. The motor drives an outer magnetic rotor, and the magnetic field penetrates a non-metallic isolation shell (such as PEEK or Ceramics) to drive the inner magnetic rotor (impeller), which is encapsulated in fluoroplastics, into synchronous rotation.
- Advantages: It completely eliminates the shaft seal, achieving total containment of the medium. It is particularly suitable for transporting high-risk, flammable, or highly toxic corrosive liquids.
Lined Centrifugal Pump
- Working Principle: Combines the mechanical strength of metal with the corrosion resistance of plastic. The pump casing is typically made of Cast Iron or Carbon Steel, while the internal wetted parts (impeller, casing lining) are lined with a thick layer of fluoroplastics (such as PTFE, PFA, or FEP) via a molding process.
- Advantages: The "Steel-Lined-Fluorine" design can withstand pipeline pressure while resisting corrosion from almost all chemical media, and the cost is typically lower than solid alloy pumps.
Key Features of Corrosion Resistant Pumps
- Chemical Inertness: Wetted parts made from PTFE (Teflon), PFA, or PVDF remain stable and unreactive even when exposed to harsh oxidizers and solvents.
- Structural Integrity: Metal-armored designs ensure the pump retains its shape and pressure-holding capability even under high temperatures, preventing plastic deformation.
- Purity Assurance: High-purity fluoroplastic materials prevent the leaching of metallic ions, making these pumps ideal for semiconductor and pharmaceutical applications where fluid purity is critical.

Key Selection Considerations for Corrosion Resistant Pumps
- Chemical Composition & Concentration: Different concentrations affect materials differently (e.g., concentrated sulfuric acid is compatible with certain metals, while dilute acid requires plastics). Always verify compatibility charts.
- Operating Temperature: Temperature accelerates corrosion and softens plastics. Ensure the selected lining material (e.g., PFA vs. PP) can handle the maximum process temperature.
- Solids Content: If the corrosive fluid contains particles, standard lined pumps may wear out. Abrasion-resistant linings (like UPE) or specialized open impellers are required.
- System Pressure: Ensure the pump casing is rated for the system's design pressure to prevent liner collapse or casing rupture.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between a plastic pump and a lined pump?
A solid plastic pump is made entirely of plastic and is limited in pressure and temperature. A lined pump has a metal shell for strength and a plastic lining for corrosion resistance, allowing for higher operating limits.
Q2. Can these pumps handle Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)?
Yes, but standard ceramic shafts or glass parts will be dissolved by HF. You must specify silicon carbide (SiC) or carbon internals when ordering for HF applications.
Q3. Is Stainless Steel 316L enough for corrosion resistance?
316L is good for many mild acids but fails quickly with Hydrochloric Acid or hot Sulfuric Acid. In these cases, Fluoroplastic (PTFE/PFA) lined pumps or Hastelloy pumps are required.